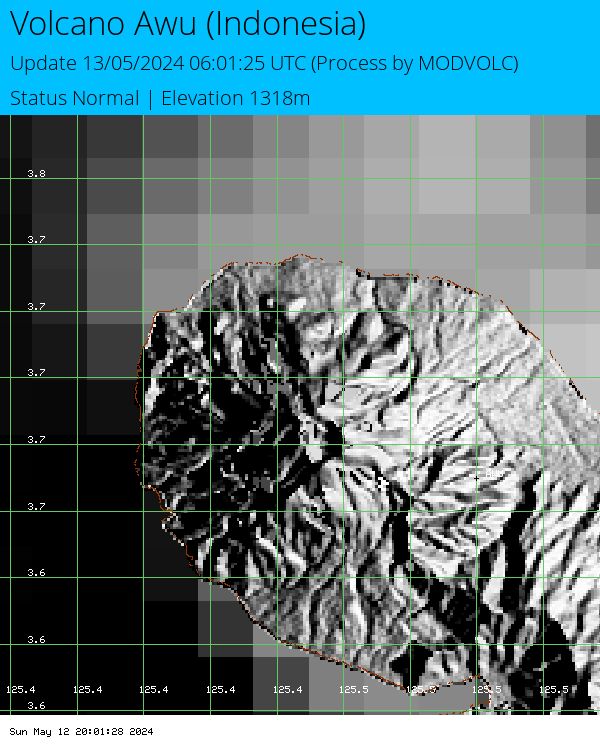
Awu (Indonesia)
Status Normal Eruption 2004 1318m
Stratovolcano (Subduction zone / Oceanic crust (< 15 km))

The massive Gunung Awu stratovolcano occupies the northern end of Great Sangihe Island, the largest of the Sangihe arc. Deep valleys that form passageways for lahars dissect the flanks of the volcano, which was constructed within a 4.5-km-wide caldera. Powerful explosive eruptions in 1711, 1812, 1856, 1892, and 1966 produced devastating pyroclastic flows and lahars that caused more than 8000 cumulative fatalities. Awu contained a summit crater lake that was 1 km wide and 172 m deep in 1922, but was largely ejected during the 1966 eruption.
A shallow lake partially fills the summit crater of Awu volcano in this 1995 view. Gunung Awu volcano, one of the deadliest in Indonesia, is cut by deep valleys that form passageways for lahars dissect the flanks of the 1320-m-high volcano. Powerful explosive eruptions in 1711, 1812, 1856, 1892, and 1966 produced devastating pyroclastic flows and lahars that caused more than 8000 fatalities.
Photo by Kristianto, 1995 (Centre of Volcanology & Geological Hazard Mitigation, Volcanological Survey of Indonesia).
Last updated 2024-04-20 04:23:00